We’ve all been there—stepping onto the scale and letting that number dictate our mood and self-worth. But what if I told you that the scale tells an incomplete story? While it measures your total weight, it doesn’t distinguish between muscle, fat, bones, and water, leaving you with a potentially skewed perception of your health.
This article aims to broaden your understanding of body composition as a more nuanced and accurate measure of health. We will explore its components, its importance, and how you can use this knowledge to make informed lifestyle choices.
The Limitations of the Scale
Weight, as a standalone metric, can be incredibly misleading. When you step onto a scale, the number you see is a sum total of various components: muscle, fat, bones, and water. This amalgamated figure doesn’t distinguish between these elements, leaving you with an incomplete picture of your health. For example, a person who weighs 70 kilograms could have a higher muscle mass and lower fat percentage than another individual with the same weight but a higher fat percentage. The scale doesn’t reveal these nuances, which are crucial for a comprehensive health assessment.
One of the most pervasive misconceptions is the belief that losing weight is synonymous with better health. While weight loss may be beneficial for those who are overweight or obese, it’s not a one-size-fits-all indicator of well-being. For instance, rapid weight loss can lead to muscle degradation, nutritional deficiencies, and other health issues. Conversely, weight gain in the form of increased muscle mass can be a positive development. These examples illustrate why the scale can be a poor arbiter of health, often leading to misguided goals and potentially harmful behaviors.
It’s crucial to understand that weight is merely one aspect of your overall health profile. Other factors, such as cardiovascular fitness, metabolic rate, blood sugar levels, and mental well-being, also play significant roles. Relying solely on weight as a measure of health is akin to evaluating the performance of a car by only considering its speed, ignoring other vital metrics like fuel efficiency, safety features, and engine health.
What is Body Composition?
Defining Body Composition
Body composition refers to the proportion of fat and non-fat mass in your body. Unlike weight, which amalgamates all these components into a single, often misleading number, body composition breaks it down into distinct categories. These categories typically include fat mass, lean mass (which encompasses muscles, organs, and blood), bone density, and water weight. By analyzing these individual components, you get a more nuanced and accurate picture of your overall health.
Components of Body Composition
Fat Mass
Fat is essential for storing energy, protecting organs, and regulating hormones. However, excessive fat, particularly visceral fat around the abdomen, can lead to a host of health issues like diabetes, heart disease, and high blood pressure.
Lean Mass
This includes muscles, organs, and blood. Muscles are metabolically active tissues that help in movement, blood circulation, and regulating metabolic rate. A higher proportion of lean mass generally indicates better physical fitness and metabolic health.
Bone Density
Your bones provide structure and protect vital organs. Bone density is a measure of the strength of your bones. Low bone density can lead to conditions like osteoporosis, making you more susceptible to fractures.
Water Weight
The human body is approximately 60% water. Water weight can fluctuate due to diet, salt intake, menstrual cycle, and other factors. While it’s a less stable component, significant changes in water weight can indicate underlying health issues.
How to Improve Body Composition
The Role of Lifestyle Changes
Improving your body composition is not a one-off event but a sustained commitment to lifestyle changes. While understanding your body composition is the first step, the actionable part comes in the form of diet and exercise adjustments tailored to your specific needs. It’s essential to consult healthcare professionals like Registered Dietitians (RD) for personalized advice, as they can provide insights based on accurate body composition measurements and medical history.
The Importance of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is foundational for improving body composition and goes beyond just macronutrients like proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. Protein is crucial for muscle repair and growth, aiding in increasing lean mass and boosting metabolic rate. Healthy fats are essential for hormone production and can assist in reducing body fat when consumed in moderation. Complex carbohydrates provide sustained energy, aid in digestion and fat loss. It’s also vital to include micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals in your diet. For example, essential vitamins like Vitamin D contribute to bone health, B-vitamins are crucial for energy metabolism, and minerals like calcium and magnesium are vital for maintaining bone density. By incorporating a balanced mix of macronutrients along with essential vitamins and minerals, you’re not only improving your body composition but also fortifying your overall health at a cellular level.
The Power of Exercise: Strength Training and Cardio
Exercise is the other pillar of improving body composition. Strength training exercises, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises, are crucial for building lean muscle mass. Muscle is metabolically active tissue, meaning it burns calories even at rest, thereby improving your metabolic rate. On the other hand, cardiovascular exercises like running, swimming, or cycling are effective for burning calories and reducing fat. A combination of both is often the most effective strategy for improving body composition.
A Holistic Approach
It’s important to note that improving body composition is not just about reducing fat or gaining muscle in isolation. The goal is a balanced improvement, which often involves both. For instance, reducing fat while simultaneously increasing lean mass will result in a more balanced body composition, improving not just your appearance but also your overall health and well-being.
Measuring Body Composition
The Importance of Professional Assessment
Before diving into the various methods of measuring body composition, it’s crucial to note that these assessments should ideally be conducted by healthcare professionals, such as registered dietitians or medical doctors. Accurate measurement and interpretation of body composition are complex tasks that require specialized knowledge and skills. Incorrect measurements can lead to misleading results, which could, in turn, result in ineffective or even harmful health interventions.
Various Methods of Measurement
Skinfold Calipers

– What it is: This method involves using calipers to measure the thickness of skinfolds at various parts of the body.
– Pros: It’s relatively simple, quick, and cost-effective.
– Cons: The accuracy can vary based on the skill of the person conducting the test and may not be as reliable for individuals with higher body fat percentages.
Bioelectrical Impedance

– What it is: This technique measures the resistance of body tissues to the flow of a small electrical signal, which is then used to estimate body composition.
– Pros: It’s non-invasive, quick, and relatively easy to perform.
– Cons: The results can be affected by various factors such as hydration levels, recent food intake, and skin temperature, requiring careful control of these variables for accurate measurement.
DEXA Scan (Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry)
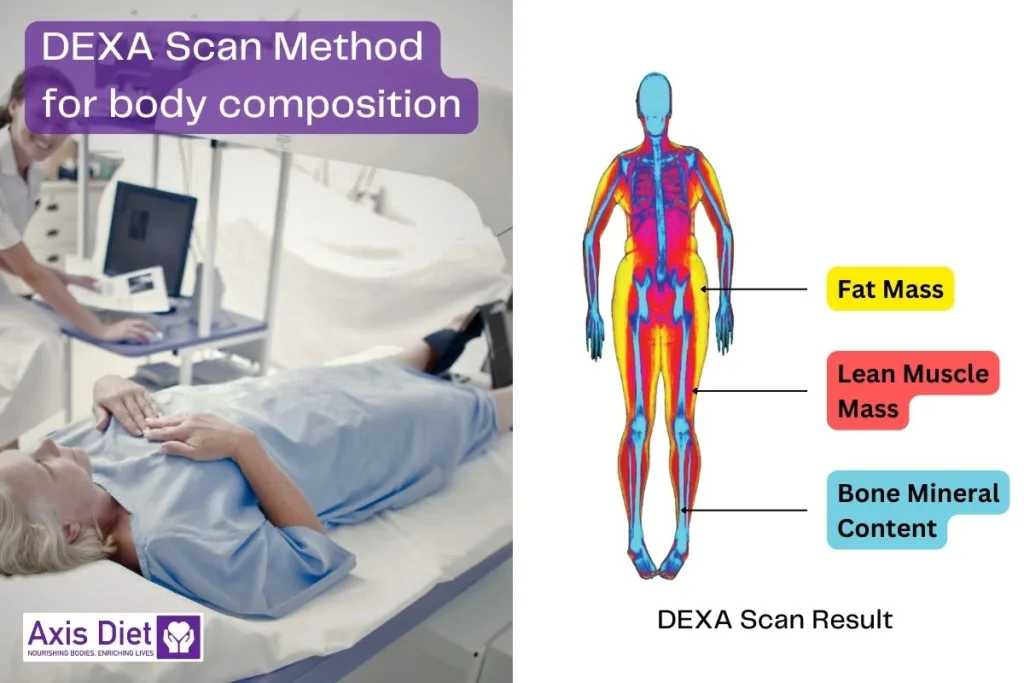
– What it is: This is a medical imaging technique that uses X-rays to measure bone density and body composition.
– Pros: It’s highly accurate and can provide detailed information, including regional body fat distribution.
– Cons: It’s more expensive, less accessible, and exposes the individual to a small amount of radiation.
Making an Informed Choice
Each method comes with its own set of advantages and limitations, and the best choice often depends on your specific needs, the availability of facilities, and the expertise of the healthcare professionals involved. Regardless of the method chosen, it’s crucial that the assessment is conducted and interpreted by qualified professionals to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Conclusion
The central message is clear: understanding your body composition offers a more accurate, nuanced, and actionable view of your health compared to merely focusing on weight. It allows you to identify specific areas that require attention, be it reducing fat, increasing lean mass, or improving bone density. This targeted approach enables you to make informed decisions that lead to better health outcomes.
As we move forward in our health journeys, let’s shift our focus from the narrow lens of weight to the broader, more informative panorama of body composition. By doing so, we adopt a more holistic approach to health and wellness—one that considers the complexities of the human body and allows for more personalized, effective interventions.






[…] species, thereby encouraging their growth and activity. This selective feeding supports a more healthful composition of the gut microbiome. The fermentation of prebiotics produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), […]
[…] gut microbiota can also influence our mental wellbeing. Studies have found correlations between the composition of the gut microbiota and mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety. For instance, certain beneficial bacteria are often found […]