Ever wonder why phrases like “trust your gut” or “I have a gut feeling” are so ingrained in our language and intuition? These sayings are not just metaphorical; they hint at a profound truth about the human body that science is only beginning to unravel. The connection between our gut and brain is a fundamental aspect of our physiology, influencing not just our physical health but our thoughts, emotions, and decision-making processes, also known as the Gut-Brain Axis. This intricate relationship explains why our “gut feelings” can sometimes seem to guide us more accurately than our rational thoughts.
Understanding the gut-brain axis is not just an academic pursuit; it’s a critical exploration into how two of our body’s major systems communicate and control much of our daily lives. Recent advancements in science have shed light on how this connection affects everything from our mood and stress levels to our overall well-being. This discovery has led to a growing interest in how we can influence this relationship for the better, primarily through our diet.
In previous discussions, such as “What are Prebiotics & Probiotics?” and “How Probiotics and Prebiotics Work Together?“, we delved into the foundational elements of gut health. These articles set the stage for understanding the beneficial bacteria that inhabit our gut and how they interact with the food we consume to support our health. Now, we advance this exploration by diving into the complexities of what is known as the gut-brain axis.
This connection between our cognitive functions and digestive system is not only fascinating but also a testament to the body’s interconnectedness. As we peel back the layers of the gut-brain axis, we realize that to truly care for our minds, we must also nurture our guts. The interplay of prebiotics and probiotics plays a crucial role in this process, offering a pathway to not just better physical health, but improved mental clarity and emotional resilience.
Understanding the Gut-Brain Axis
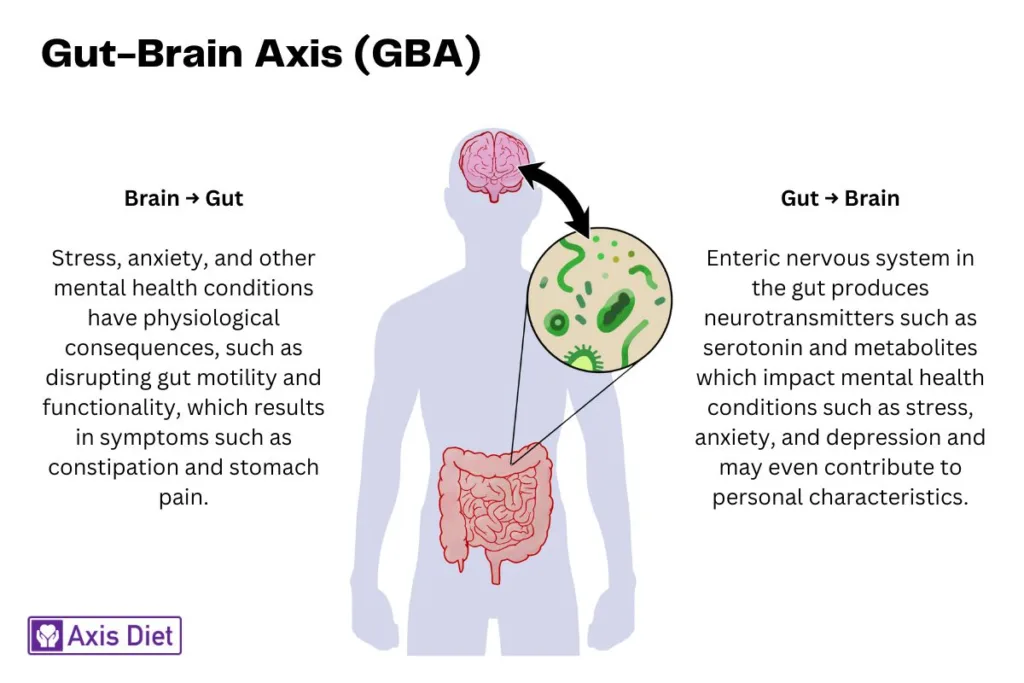
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication system involving neural, hormonal, and immunological signals. It’s fascinating to realize that your gut houses around 500 million neurons connected to your brain through nerves, most notably the vagus nerve. This connection allows for a continuous exchange of signals that can influence our emotional and psychological state.
Our gut is teeming with trillions of microbes, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, collectively known as the gut microbiota. These microbes produce various chemicals and neurotransmitters that can affect brain function. For instance, a significant portion of the body’s serotonin, a neurotransmitter associated with feelings of happiness, is produced in the gut.
Research has shown that gut microbes play a pivotal role in regulating mood and could be linked to mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression. Probiotics, often referred to as “good” bacteria, have been found to improve symptoms of stress, anxiety, and depression, highlighting the importance of a balanced gut microbiota for mental health.
Nutritional Influence on the Gut-Brain Axis
The foods we eat significantly impact our gut microbiota, and by extension, our mental health. A diet rich in specific nutrients can support and enhance the gut-brain axis, leading to improved mood, cognitive function, and overall well-being. Let’s expand on the critical components of such a diet and how they benefit both gut health and brain function.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fats, particularly those found in oily fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, are not only crucial for brain health but also play a significant role in maintaining a healthy gut microbiota. These essential fatty acids are integral to the structure of brain cells, facilitating communication between them. Moreover, omega-3s have been shown to increase the diversity of the gut microbiome, which is vital for reducing inflammation—a common culprit behind many mental health disorders, including depression and anxiety. Incorporating omega-3-rich foods into your diet can help fortify the brain against stress and inflammation, promoting a sense of well-being.
Fermented Foods
Fermented foods are a treasure trove of beneficial microbes that can transform the landscape of our gut microbiota for the better. Foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi introduce a variety of probiotics into the gut, which can help balance the microbiome and enhance its resilience against pathogens. These beneficial bacteria produce neurotransmitters, including serotonin and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), directly influencing mood regulation and reducing anxiety. By incorporating fermented foods into your diet, you can directly support your mental health through your gut.
High-Fiber Foods
Dietary fiber found in whole grains, nuts, seeds, fruits, and vegetables acts as a prebiotic, providing essential nourishment for beneficial gut bacteria. These prebiotic fibers promote the growth of healthy bacteria, which in turn produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, propionate, and acetate. SCFAs have been shown to strengthen the blood-brain barrier, reduce inflammation, and support the production of neurotransmitters. A high-fiber diet ensures a thriving gut microbiota, which supports cognitive functions and emotional health.
Polyphenol-Rich Foods
Polyphenols, found in abundance in foods like berries, nuts, dark chocolate, olive oil, and green tea, are micronutrients with potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. When consumed, these compounds are partially digested by gut bacteria, enhancing microbial diversity and growth. Polyphenols can also cross the blood-brain barrier, where they exert neuroprotective effects, including the reduction of oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain. This can lead to improved cognitive functions and a lower risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Tryptophan-Rich Foods
Tryptophan, an essential amino acid found in foods like turkey, eggs, cheese, and tofu, is a precursor to serotonin, a neurotransmitter that plays a pivotal role in mood regulation. The gut microbiota influences the availability of tryptophan, which can affect serotonin production both within the gut and the brain. A diet high in tryptophan can support serotonin synthesis, promoting feelings of happiness and relaxation.
By emphasizing these nutritional components in your diet, you can harness the power of the gut-brain connection to support both mental and physical health. This synergy between what we eat and how we feel underscores the importance of a balanced, nutrient-rich diet as a foundation for overall well-being.
The Path to a Healthier Mind Through the Gut
Enhancing the practical tips section involves delving deeper into how incorporating probiotics and prebiotics into your diet not only supports gut health but also promotes mental well-being through the gut-brain axis. Here’s an expanded view of each tip with a focus on its impact on mental health:
1. Start Your Day with a Probiotic Boost
Beginning your day with probiotic-rich foods like yogurt or kefir can help establish a healthy gut microbiome from the moment you start your day. This is crucial because a balanced microbiome can enhance mood regulation and stress response, thanks to the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin, a significant portion of which is produced in the gut. Including these foods in your breakfast routine can provide a steady foundation for mental wellness throughout the day.
For more information on which probiotic foods to include in your diet, check out “The Best Probiotic Foods for Your Gut Health.” This article provides a comprehensive guide to probiotic-rich foods that are beneficial for your gut and, consequently, your mental health.
2. Snack on Fermented Foods
Integrating fermented snacks such as sauerkraut, kimchi, or tempeh into your diet not only diversifies your gut microbiota but also introduces beneficial bacteria that can improve brain health. Fermented foods can modify the composition of gut bacteria, leading to an enhanced production of mood-regulating neurotransmitters. This alteration in the gut microbiome can help alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression, making fermented snacks a powerful tool in your mental health toolkit.
3. Increase Fiber Intake Gradually
Fiber acts as a prebiotic, providing food for beneficial gut bacteria. Gradually increasing your intake of fiber-rich foods ensures that your gut microbiota flourishes, positively impacting your mood and cognitive function. A well-fed microbiome produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, which have been shown to reduce inflammation and are linked to reduced stress levels and improved mental health. Incremental increases help avoid digestive discomfort, ensuring a smooth transition to a gut-friendly diet.
To discover the best sources of prebiotic fibers, refer to “10 Best Prebiotics Food You Should Eat.” This article will guide you through the top prebiotic foods that can enhance your gut health and, by extension, support your mental well-being.
4. Diversify Your Diet
A varied diet ensures a wide range of prebiotics and probiotics, fostering a diverse microbiome. This diversity is key to gut health, which in turn influences brain health through the gut-brain axis. A diverse microbiome can enhance the resilience of your gut flora, making it more capable of combating stress and inflammation, both of which can negatively affect mental health. Embracing a variety of foods enriches your microbiome, which supports emotional well-being and cognitive function.
5. Consider Supplements
While whole foods are the best source of prebiotics and probiotics, supplements can fill gaps in your diet or offer a concentrated dose of beneficial bacteria and fibers. This can be particularly useful for individuals with dietary restrictions or those who find it challenging to consume a wide variety of probiotic and prebiotic foods. Supplements can ensure that your gut microbiome receives the necessary components to support mental health, helping to regulate mood and alleviate symptoms of stress and anxiety. Consulting with a healthcare provider ensures that you choose the right supplements to complement your dietary needs and health goals.
Wrapping Up
As we conclude our exploration of the gut-brain axis, it’s clear that this intricate connection plays a pivotal role in our overall health and well-being. The profound impact of our gut microbiota on mental health underscores the importance of nurturing our gut through mindful nutritional choices. By incorporating a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fermented foods, high-fiber foods, polyphenol-rich foods, and tryptophan, we can support this vital connection, promoting mental clarity, emotional stability, and a heightened sense of well-being.
As we continue to uncover the mysteries of the gut-brain axis, let us embrace the wisdom of “trusting our gut” not just as a metaphor but as a practical guide to living healthier, happier lives. The journey towards understanding and optimizing the gut-brain connection is an ongoing one, filled with potential for personal growth and wellness. By making informed choices about our diet and lifestyle, we can nurture this essential link and enjoy the profound benefits it brings to our mental and physical health.
In closing, let the knowledge of the gut-brain axis inspire you to consider your gut health as an integral part of your mental health strategy. The choices we make at the dining table can resonate through every aspect of our lives, influencing our mood, cognition, and overall well-being. Here’s to a healthier gut, a brighter mind, and a more vibrant life.
References:
- Polyphenols-gut microbiota interplay and brain neuromodulation
- Tryptophan Metabolism: A Link Between the Gut Microbiota and Brain
Axis Diet is dedicated to empowering individuals with knowledge and practical advice for healthier living. Our articles, grounded in research and expert insights, aim to simplify complex nutritional concepts, offering a comprehensive understanding of various aspects of diet and wellness. While these articles are informative and a great starting point for anyone looking to improve their health, they are for informational purposes only.
For personalized, professional guidance tailored to your unique health needs, we encourage you to consult with Axis Diet’s registered dietitians. Reach out to us at https://www.axisdiet.com/contact/ for expert personalized guidance on your nutritional journey.






[…] producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). These SCFAs benefit the immune system and may even influence mental health. Foods like cooked and cooled rice, potatoes, green bananas, and whole grains such as barley are […]